Efficient Image Naming with Interpolation
What is Interpolation?
Interpolation is a powerful technique that dynamically generates image names by inserting specific values into a predefined expression. This method is highly efficient as it automates the naming process and ensures consistency across your files. You can use interpolation to include details like dates, formats, indices, scales, and dimensions in your image names.
When to Use the Interpolation Function
The interpolation function is a powerful tool for customizing image names based on specific attributes such as dates, formats, indices, scales, and dimensions. However, if each of your image assets already has a unique and descriptive name, like ‘star-icon.png’ or ‘banner-pic.png’, there’s no need to use this function. The interpolation feature is especially useful when you want to standardize and structure the naming of multiple images, making it an ideal choice for optimizing your workflow and file organization.
Access Name Settings
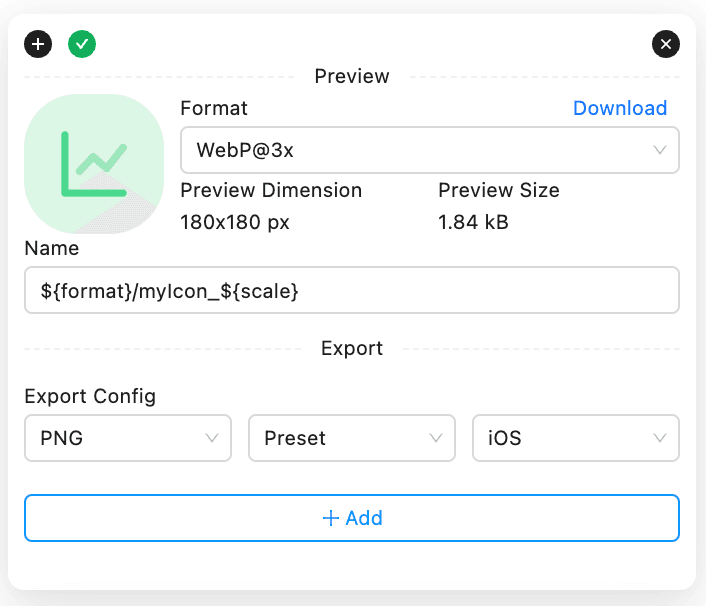
Within the InnoExport interface, there is a input field called Name just below the preview image of each of layers you select. Or, you can use the same field in the Batch Edit panel and Preset Config section in the Config panel to batch edit names for all layers you select.
By default, this field is filled by the name of the layer’s name and left blank in the Batch Edit panel, which means it has no effect to the name of each layer you select. You can change the value of this field to whatever you want and its value will be used as the name of image file you export.
Write an Interpolation Expression
Interpolation expressions in InnoExport are constructed using template strings, similar to JavaScript ES6’s template strings. All you need is to fill a expression(e.g. ${name}_${index}_${format}) in the Name input field. These expressions allow you to dynamically generate image names based on various parameters. Below are some examples of interpolation expressions with explanations of what each parameter generates:
Example 1: Basic Expression
Expression: ${name}
Giving Values:
- `${name}` = "star-icon.png"
Generated Image Name: "star-icon.png"Explanation: In this basic expression, ${name} is set to “star-icon.png,” so the generated image name remains the same as the asset’s original name.
Example 2: Adding Index and Format
Expression: ${name}_${index}_${format}
Giving Values:
- `${name}` = "logo"
- `${index}` = 3
- `${format}` = "png"
Generated Image Name: "logo_3_png.png"Explanation: This expression combines ${name}, ${index}, and ${format}. In this case, it results in an image name that includes the asset’s name, the index 3, and the chosen format “png”.
Example 3: Including Scale and Dimensions
Expression: ${name}@${scale}x_${width}x${height}
Giving Values:
- `${name}` = "banner"
- `${scale}` = 2
- `${width}` = 800
- `${height}` = 600
Generated Image Name: "banner@2x_800x600.png"Explanation: In this expression, ${name}, ${scale}, ${width}, and ${height} are used. The generated image name includes the asset’s name “banner”, its scale 2 and dimensions “800x600”.
Example 4: Using Datetime and Format
Expression: ${format}_${datetime}
Giving Values:
- `${format}` = "jpg"
- `${datetime}` = "Oct 15, 2023 15:45:00"
Generated Image Name: "jpg_Oct 15, 2023 15:45:00.jpg"Explanation: This expression combines ${format} and ${datetime}. It generates an image name that includes the chosen format “jpg” and the date and time “Oct 15, 2023 15:45:00” based on the default locale string of the user’s browser.
Example 5: Using a Dictionary with ’/’
Expression: ${format}/${name}
Giving Values:
- `${name}` = "product-image"
- `${format}` = "png"
Generated Image Name: "png/product-image.png"
Explanation: In this expression, a dictionary is created using the / character. This structure is valuable when you want to categorize and organize exported images by different attributes, making it easier to manage and find specific files. For instance, you might use a dictionary to group images by format and name, enhancing your file organization in the export result.
Interpolation Parameters
Here’s a detailed explanation of each available parameter for constructing interpolation expressions:
${name}: Represents the name of the asset. This parameter is only available in the preset settings and will be replaced with the original asset name.${index}: Represents the index of the asset selected, starting from 1. It allows you to include the asset’s position in the list.${scale}: This parameter represents the scale of the image and is only available when exporting PNG, JPG, AVIF, or WebP images.${width}: Represents the width of the image in pixels and is only available when exporting PNG, JPG, AVIF, or Web images.${height}: Represents the height of the image in pixels and is only available when exporting PNG, JPG, AVIF, or Web images.${format}: Represents the selected export format. Currently, only PNG, JPG, WebP, AVIF and SVG are supported formats.${datetime}: This parameter represents the export time as a string. It uses the default locale string of the user’s browser and is useful for including timestamps in image names.${datetime:CUSTOM_FORMAT}: Similar to${datetime}except use your custom date-time foramt(e.g.${datetime:YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss}). All available formats are listed below:
| Format | Output | Description |
|---|---|---|
YY | 18 | Two-digit year |
YYYY | 2018 | Four-digit year |
M | 1-12 | The month, beginning at 1 |
MM | 01-12 | The month, 2-digits |
MMM | Jan-Dec | The abbreviated month name |
MMMM | January-December | The full month name |
D | 1-31 | The day of the month |
DD | 01-31 | The day of the month, 2-digits |
d | 0-6 | The day of the week, with Sunday as 0 |
dd | Su-Sa | The min name of the day of the week |
ddd | Sun-Sat | The short name of the day of the week |
dddd | Sunday-Saturday | The name of the day of the week |
H | 0-23 | The hour |
HH | 00-23 | The hour, 2-digits |
h | 1-12 | The hour, 12-hour clock |
hh | 01-12 | The hour, 12-hour clock, 2-digits |
m | 0-59 | The minute |
mm | 00-59 | The minute, 2-digits |
s | 0-59 | The second |
ss | 00-59 | The second, 2-digits |
SSS | 000-999 | The millisecond, 3-digits |
Z | +05:00 | The offset from UTC, ±HH:mm |
ZZ | +0500 | The offset from UTC, ±HHmm |
A | AM PM | |
a | am pm |